Many people wonder why the human body is unable to destroy cancer cells.
Just like nature, the body is smart. Many people wonder how it is possible for the body to not detect abnormal cancer cells. Therefore destroy or eliminate cancer cells in some way to keep the body safe. Although this is ideal But that’s not what happened. Usually, when cancer appears in a person It is often quite aggressive and often life-threatening for people suffering from cancer.
A good question is: “Why doesn’t our body recognize and eliminate cancer cells like we do? Bacteria or viruses? The answer is that most cancer cells are detected and eliminated by our immune system. Cells in our immune system called natural killer cells are responsible for finding abnormal cells so that other cells can treat them. Our immune system can eliminate them. Cancer cells can live. Either by evading detection (They disguise themselves in various ways) or by inactivating immune cells that reach the site.
The immune system’s ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells is believed to be the cause of this rare but well-documented phenomenon. Some types of cancer disappear without treatment. (Relieving symptoms of cancer on its own) This process is also at the center of a new cancer treatment called immunotherapy.
Cancer cells are constantly changing.
When cancer develops Cells will not remain the same. But mutations can occur continuously.This is why resistance to chemotherapy and targeted therapy develops early. Cancer cells develop mutations that allow them to avoid the harmful effects of these treatments.
Changes in cancer cells are very important in treatment. For example, breast cancer that is positive for estrogen receptors may be negative when it recurs or spreads. It also helps explain how different parts of cancer cells develop. of the tumor may be different. This is called “Difference” and is also important in diagnosis and treatment.
What are killer cells?
Natural killer cells are aggressive cells of the immune system that play a key role in fighting cancer and virus-infected cells. Although T cells (A subtype of white blood cell that plays an important role in the immune system and fighting cancer) is also important in cancer. But natural killer cells are The “first responders” were on scene before T Cell was called.
Natural killer cells are a type of lymphocyte, which is a type of white blood cell in the body. Killer cells are thought to make up 10% or less of the body’s white blood cells.
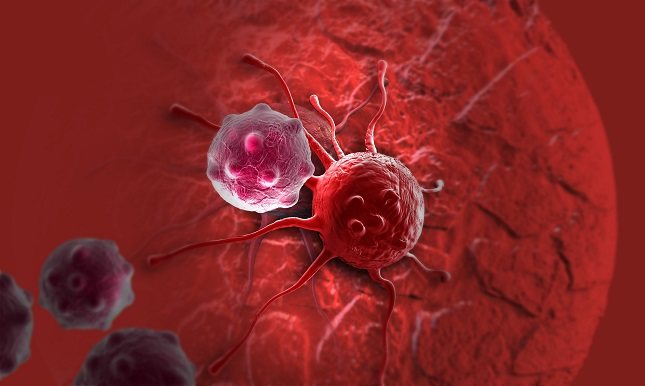 Killer cells (Natural Killer in English) are a type of white blood cell.
Killer cells (Natural Killer in English) are a type of white blood cell.How do killer cells work in immunity?
Because it is part of the natural immune system Natural killer cells therefore do not need to recognize specific abnormalities (antigens) in virus-infected cells or cancer cells. This is different from some of the functions of immune cells that result from immune memory. If cells don’t recognize it as a normal part of the body, Killer cells can perform one of two functions:
- Cytotoxic (cell destruction) Killer cells can be toxic to cells. In this process It enters the cell and releases toxic granules into the abnormal cell. These granules create holes in the cell membrane. Let them swell and crack. Kills abnormal cells, sometimes instead of exploding Cells may undergo a controlled death process called apoptosis.
- immune regulation Natural killer cells can also be used as a form of immune regulation. In this process Cells control the functioning of the immune system by producing substances called cytokines. Causes the death of cancer cells or cells infected with viruses.